Geographic Extent ★★★★
To quickly determine the general location of spatial features included in a cited resource it is useful that the extent information is provided in such a way so that the geographical extent of the resource can be easily understood.
| Element Name | geographicElement |
| Parent | MD_Metadata.identificationInfo>MD_Identification.extent |
| Class/Type | EX_GeographicExtent |
| Governance | Common ICSM, Domain |
| Purpose | Discovery |
| Audience | machine resource - ⭑ ⭑ ⭑ ⭑ |
| general - ⭑ ⭑ ⭑ ⭑ | |
| resource manager - ⭑ ⭑ | |
| specialist - ⭑ ⭑ ⭑ (higher if domain specific placenames are used) | |
| Metadata type | descriptive |
| ICSM Level of Agreement | ⭑ ⭑ ⭑ |
Definition
A description of the spatial area of the resource. These may be of the type Bounding Box, Geographic Description, or Bounding Polygon.
ISO Obligation
- There can be zero to many [0..*] Geographical Extent packages for the cited resource in the Resource Extent package. These may be of the type Bounding Box (EX_GeographicBoundingBox), Geographic Description (EX_GeographicDescription), or Bounding Polygon (EX_BoundingPolygon).
Discussion
Every metadata record describing geographic resources should contain descriptions that explain the area of interest of the resource. These may be in the form of place names, bounding box coordinate values and lastly, bounding polygons. With these, those searching for resources can be provided with a quick visual of the usable location of the resource. Catalogue software can use these descriptions to analyse and narrow searches to particular areas of interest.
The use of multiple geographic extents is recommended for more complicated geometries, including exclusion areas.
As these extents are meant to be used to give a general rough comparison to other geospatial data from sources, coordinates values should be captured in WGS 84 (EPSG 4326)
Best Practice Recommendations
Therefore - it is strongly recommended that to support the discovery of resources, every metadata record that describes a geographic resource contains geographic descriptions of the area of interest for the resource. At a minimum one description needs be in bounding box coordinate values. If there be any exclusion areas, the use of the boolean extentTypeCode (set to “0”) is recommended.
The MDWG recommends populating as many instances of Geographical Extent packages as needed to give a common understanding of the spatial coverage of the cited resource.
Recommended Sub Types
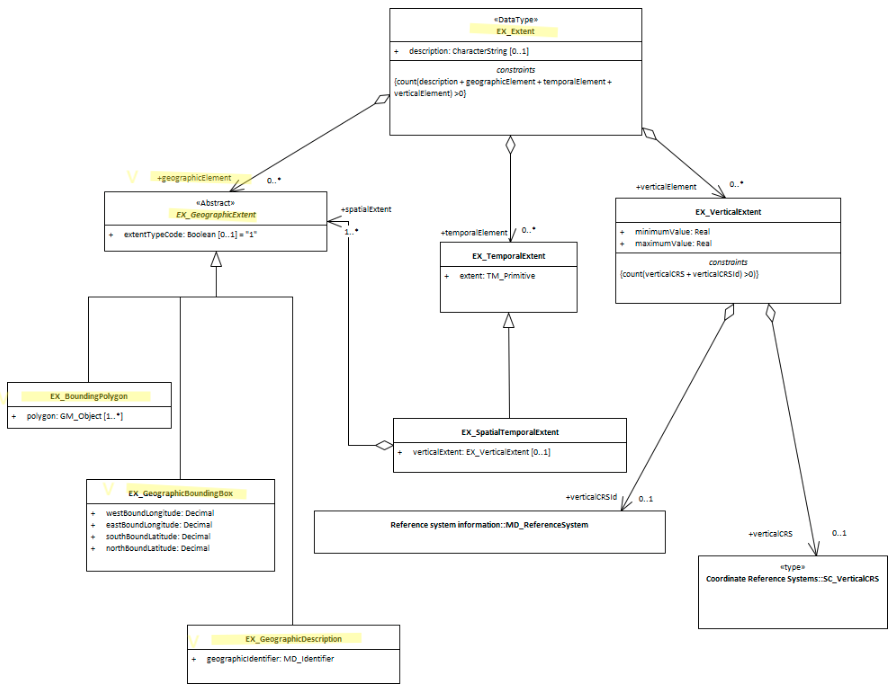
EX_GeographicExtent is an abstract class that is expressed by one of the three options
- Geographic Bounding Box - (class - EX_GeographicBoundingBox) highly recommended for resources with geographic extent. An approximate geographic position of the resource using EPSG 4326 coordinate pairs with a precision of up to two decimal places
- Geographic Description - (class - EX_GeographicDescription) highly recommended for resources with geographic extent. A description of the geographic area using identifiers
- Bounding Polygon - (class EX_BoundingPolygon) optional - not recommended by MDWG except in cases where the other options do not suit
- Use extentTypeCode (Boolean) [0..1] witha value of “0” to indicate exclusions
Also Consider
- EX_GeographicExtents is an abstract class that can be express three ways:
- EX_GeographicBoundingBox - at least one of these should be present for resources that describe geographic resources
- EX_GeographicDescription - One of these should be present for resources that describe geographic resources
- EX_BoundingPolygon While very useful, particularly in describing irregular areas, this element is not described by the MDWG as a recommended element due to the difficulties that many systems have in implementing it.
- EX_Extent The class that contains all extent information about the cited resource - vertical, geographical or temporal.
- EX_TemporalExtent Contains temporal extent information for the cited resource
- EX_VerticalExtent - captures the vertical range of a resource.
Other Discussion
data.gov.au guidance Free text with a mandatory requirement to use one of the following:
- a point/polygon (WKT);
- an administrative boundary API; or,
- a reference URL (website address) from the National Gazetteer. Gazetteer reference URLs can be found by searching for a place at http://www.ga.gov.au/place-names/ then clicking through to the most appropriate location “Reference ID”, and then copying and pasting the URL from the page into the Geospatial field in data.gov.au.
Crosswalk considerations
Dublin core / CKAN / data.gov.au
Maps to jurisdiction or geospatial coverage
DCAT
Maps to dct.spatial
RIF-CS
Maps to Coverage/Spatial
Examples
\pagebreak
UML diagrams
Recommended elements highlighted in yellow
\pagebreak
 ISO 19115-1 Metadata Best Practice Guide
ISO 19115-1 Metadata Best Practice Guide